The Essential Guide to Shoulder Abduction and External Rotation
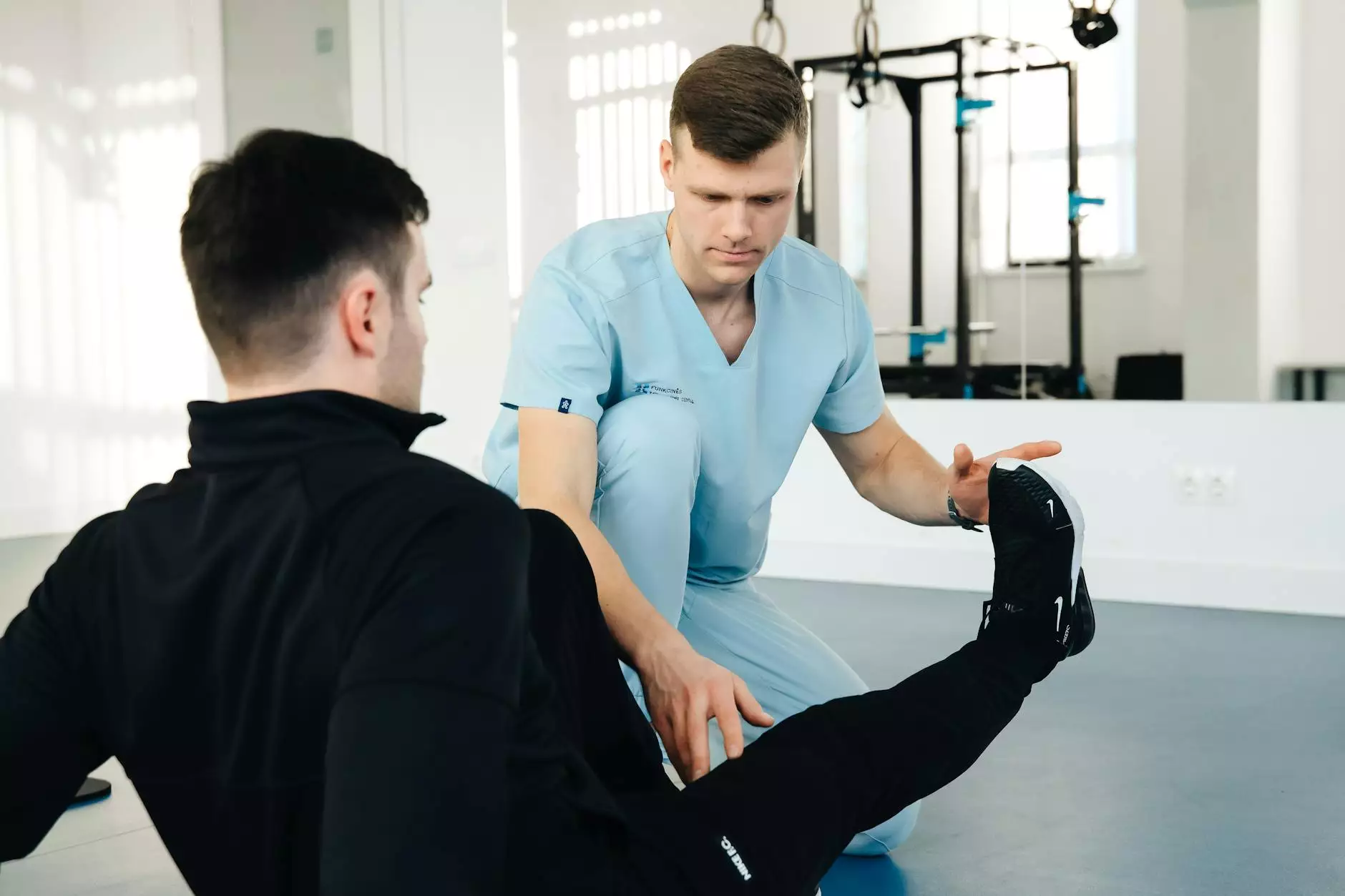

Shoulder abduction and external rotation are crucial movements that involve the shoulder joint's muscles and ligaments. Understanding these movements can significantly improve your overall health, enhance your athletic performance, and prevent injuries. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the anatomy of the shoulder, the significance of these movements, exercises to enhance these abilities, and tips for rehabilitation and injury prevention.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder joint is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the human body. It consists of three main bones: the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. The interactions between these bones and the muscles surrounding them create vast ranges of motion.
Key Components of Shoulder Anatomy
- Humerus: The long bone in the upper arm, which connects to the shoulder at the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
- Scapula: Also known as the shoulder blade, it provides stability and support for shoulder movements.
- Clavicle: Commonly known as the collarbone, it connects the arm to the body and plays a role in shoulder function.
- Rotator Cuff: A group of muscles and tendons that keep the arm bone securely in the shoulder joint and allow for a range of motions.
The Importance of Shoulder Abduction
Shoulder abduction is the movement of the arm away from the body, primarily facilitated by the deltoid muscle and the supraspinatus muscle. This action is critical for numerous daily activities and athletic performance.
Functional Benefits of Shoulder Abduction
Engaging in shoulder abduction exercises can lead to multiple benefits, such as:
- Enhanced Mobility: Improving your range of motion in the shoulder, allowing for more fluid movement in sports and everyday tasks.
- Increased Strength: Strengthening the muscles involved in shoulder movements leads to better overall stability and balance.
- Enhanced Performance: Athletes can benefit significantly from increased shoulder mobility and strength, contributing to improved performance in sports.
Understanding External Rotation of the Shoulder
External rotation of the shoulder refers to the rotation of the arm away from the body. This movement is essential for various activities, including throwing, swimming, and even lifting objects. The infraspinatus and teres minor muscles play a crucial role in facilitating this motion.
The Role of External Rotation in Shoulder Function
The benefits of shoulder external rotation include:
- Joint Stability: Helps stabilize the shoulder joint and prevents injuries during dynamic movements.
- Posture Improvement: Contributes to better shoulder alignment and posture, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
- Injury Prevention: Reinforcing external rotation can prevent common shoulder injuries, particularly for athletes.
Exercises for Shoulder Abduction and External Rotation
Regularly performing exercises focusing on shoulder abduction and external rotation can foster strength, flexibility, and endurance in the shoulder region. Here are some effective exercises:
1. Lateral Raises
This exercise targets the deltoid muscle, primarily facilitating shoulder abduction.
- How to Perform:
- Stand upright with a dumbbell in each hand.
- Lift the weights laterally (out to the sides) until they reach shoulder height.
- Lower them slowly back to the starting position.
- Repeat for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
2. External Rotation with Resistance Band
This exercise is excellent for building strength in the external rotators of the shoulder.
- How to Perform:
- Attach a resistance band to a stationary object at waist height.
- Stand lateral to the band, holding it with the hand furthest from the anchor point.
- With your elbow bent at 90 degrees, pull the band away from your body.
- Return slowly to the starting position and repeat for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
3. Dumbbell Shoulder Press
This exercise engages the entire shoulder area and contributes to enhancing both abduction and external rotation.
- How to Perform:
- Sit or stand with a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level.
- Press the weights overhead until your arms are fully extended.
- Lower the dumbbells back to shoulder level.
- Perform 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions.
Rehabilitating Shoulder Injuries
Understanding shoulder abduction and external rotation is especially critical in the context of rehabilitation. Many common injuries, such as rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, or tendinitis, can significantly impact these movements.
Common Shoulder Injuries
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: These injuries can result from repetitive overhead motions, causing pain and limiting shoulder function.
- Frozen Shoulder: This condition leads to stiffness and pain, limiting mobility in shoulder abduction and rotation.
- Shoulder Dislocations: Resulting from trauma, dislocations can significantly affect shoulder stability and movement.
Rehabilitation Strategies
Effective rehabilitation strategies should include:
- Consultation with a Professional: Always seek guidance from a qualified physical therapist or chiropractor, especially for a tailored rehabilitation program.
- Gradual Strengthening: Start with gentle stretches and gradually introduce strengthening exercises as pain diminishes.
- Consistency: Regular practice of prescribed exercises is vital for optimal recovery and long-term shoulder health.
Conclusion: Embracing Optimal Shoulder Health
In summary, understanding and engaging in shoulder abduction and external rotation exercises can lead to improved shoulder function, better athletic performance, reduced injury risks, and enhanced daily living activities. By incorporating specific exercises into your routine and prioritizing shoulder health, you can maintain robust, functional shoulders that support you at every stage of life.
At IAOM-US, we emphasize educational resources and expert guidance in health and medical fields, particularly focusing on chiropractic care and rehabilitation. By prioritizing knowledge about your body's mechanics, you empower yourself to achieve optimal health and wellness in your personal and professional life.